
In its balanced form, the equation now shows four nitrogen and six oxygen atoms on both sides of the equation. This unbalanced equation violates the law of conservation of mass, but can be remedied by the proper placement of stoichiometric coefficients so that 2N 2 + 3O 2 -> 2N 2O 3. There are two atoms each of nitrogen and oxygen on the left-hand reactant side, but the product side contains two nitrogen atoms and three oxygen atoms. In its unbalanced state, the equation does not show an equal number of nitrogen and oxygen atoms on both the left and right sides. In another example, once again involving atoms of nitrogen and oxygen, coefficients need to be added to both sides of the following unbalanced equation: N 2 + O 2 -> N 2O 3. Placing a coefficient of 2 before the product, however, will balance out the equation and is written as N 2 + O 2 -> 2NO. The nitrogen atoms and oxygen atoms on the left-hand reactant side of the equation do not equal the number of atoms on the right-hand product side. For example, this is an unbalanced equation: N 2 + O 2 -> NO. atom synonyms, atom pronunciation, atom translation, English dictionary definition of atom. The law states that the quantity of each element involved in a chemical reaction does not change. The tremendous energy of the sun which is obtained by nuclear fusion, releases trillions of neutrino every second.The need for balanced chemical equations is dictated by the law of conservation of mass. Neutrino has no charge but travels at a very high speed, similar to the speed of light, and can pass through any solid object. Neutrino: They are similar to electrons formed from nuclear reactions.John Ellis and his fellow workers discovered them in 1979. The higher the electronegativity is the more it attracts the electrons towards it. Electronegativity is affected by the atomic number and the distance between the valence electrons and its nucleus. Gluons: Also found within protons and electrons, they act as exchange particles that help transfer strong force between quarks. Electronegativity is a chemical property that measures the tendency of an atom to attract electrons towards itself.A proton contains three quarks (two up quarks and one down quark), whereas a neutron contains (two down quarks and one up quark). Quarks are of six different types: up, down, top, bottom, charm, and strange. However, their exact position in an atom cannot be measured with accuracy. They were independently discovered by Murray Gell-Mann and George Zweig in 1964. Quarks: They are fundamental subatomic particles that makeup protons and electrons.Given below is a table showing the charge, mass, and location of the three sub-atomic particles: Name of the Particle Neutrons are neutral particles with no charge but have a substantial size and mass similar to a proton. They were discovered by James Chadwick in the year 1932 and are denoted by the symbol n or n 0. Neutrons, similar to protons, are made of quarks and gluons. They are also found within the nucleus along with the protons in a tightly packed manner. Protons consist of even smaller particles called quarks and gluons.įound tightly packed with the nucleus, they make up virtually all of the mass of an atom along with the neutrons. They were discovered by Ernest Rutherford in the year 1917 and are denoted by the symbol p or p +.
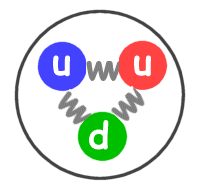
Protons are positively charged particles found within a dense region at the center of the atom called the nucleus. When the number of negatively charged electrons is equal to the number of positively charged protons, the atom is neutral in charge. Thomson discovered it in the year 1897.Įlectrons move so fast around the nucleus that their exact location within an atom cannot be determined with accuracy. The standard symbol used for an electron is e or e –.
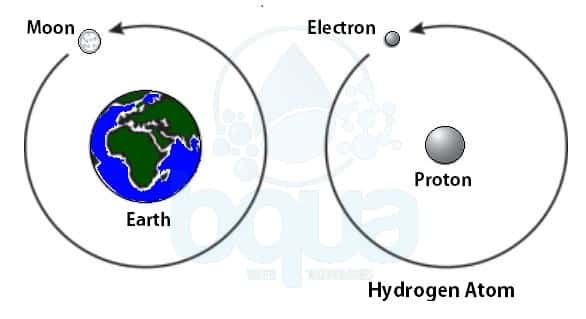
Unlike protons and neutrons, electrons are fundamental particles much smaller (almost 1800 times) in size than protons and neutrons. They are negatively charged particles that revolve around the nucleus in a fixed orbit. In contrast, electrons are found outside the nucleus in a region called the electron cloud or electron shell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Radioactive_decay-5b086ae78e1b6e003ec7903f.jpg)
Electrons and protons are found at the center of the atom within a dense region called the nucleus. All atoms except hydrogen contain three basic subatomic particles: 1) electrons, 2) protons, and neutrons.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
